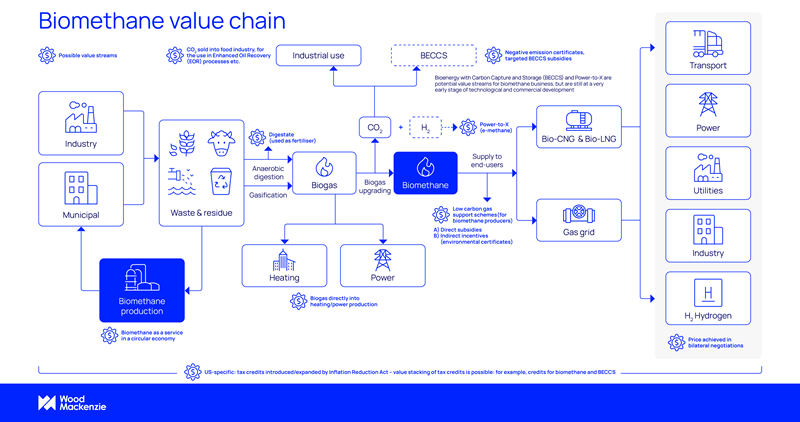
Biomethane/Renewable Natural Gas (RNG)
Wood Mackenzie helps customers understand key value streams of biomethane production
What is biomethane/RNG?
Biomethane, or renewable natural gas (RNG), is upgraded biogas, which is mostly produced through anaerobic digestion from organic feedstock including food waste, agricultural and farming waste, crops, landfill, and municipal waste.
Biomethane vs fossil natural gas
Since biomethane’s properties are nearly identical to fossil natural gas, it can be injected into the existing gas grid and used in the same applications.
Both biomethane and fossil natural gas emit carbon when combusted. However, biomethane does not introduce new carbon into the global system and therefore it is considered a low-carbon source on a net lifecycle basis. Carbon is removed from the atmosphere when the organic feedstock is grown. And, when generated from waste, biomethane production avoids massive methane emissions that would’ve occurred if waste were to degrade naturally.
Get to know the biomethane industry

Does biomethane make money? Production costs vary substantially, but the right business model allows for value stacking to improve the economics. However, you’ll need to understand the market, cost structures, cross-sector opportunities, government incentives, as well as all feedstock and technology options for a strategic approach.
Wood Mackenzie helps customers understand key value streams.

What is the potential for biomethane developments? ESG pressures and government targets are driving investments in biomethane. The industry will grow despite challenges like regulatory uncertainty, access to feedstock, and varying costs.
To navigate these challenges, Wood Mackenzie offers detailed analysis of biomethane supply and demand fundamentals, key players, and the regulatory landscape.

Can biomethane reduce emissions? RNG is increasingly compared to other decarbonisation options, not just fossil natural gas. Its versatility can help decarbonise multiple sectors, particularly those where electrification is hard and options like green hydrogen are still emerging.
Our analysis helps customers understand how biomethane contributes to decarbonisation of various demand sectors.
Why all the hype?
Despite only small supply volumes now, the biomethane/RNG industry has been increasingly attracting investments as companies are seeing biomethane as part of their integrated net zero solutions. Some governments are counting on biomethane to help improve the security of supply, reduce emissions in hard-to-decarbonise sectors, and build a circular economy while using existing natural gas infrastructure.
In addition to a variety of value-generating routes, increasingly supportive government policies make biomethane/RNG an attractive investment for producers. And for users, it can act as a direct substitute for fossil-based natural gas, be an efficient alternative to more complex decarbonisation options, and help unlock several non-energy-related benefits.
Find out more about our Biomethane/RNG Service
Our industry experts are on hand to guide you through all aspects of the biomethane/RNG industry.