How the ERCOT grid has changed over time, and the obstacles ahead
How will ERCOT cope with Texas’ rising energy demands and the complex challenges that come with a rapidly evolving energy landscape?
5 minute read
Taoxuan Luo
Market Analyst, Power & Renewables

Harindra Cherukuri
Market Associate, ERCOT

Harindra Cherukuri
Market Associate, ERCOT
Latest articles by Harindra
View Harindra Cherukuri 's full profileERCOT (Energy Reliability Council of Texas) manages the flow of electric power to 26 million Texas customers, approximately 90% of the state’s electric load. ERCOT schedules power on an electric grid that connects more than 52,700 miles of transmission lines and 1,100 generation units, performs financial settlement for the competitive wholesale bulk-power market, and administers retail switching for nearly eight million premises in competitive choice areas.
Managing these functions is critical in light of the rapid load growth in the ERCOT region. Examples of drivers of the load growth include gaining three million residents from 2000 to 2022 (US Census), accelerated growth of energy-intensive data centers in and around major population centers and increased drilling activity.
Our recent insight, Trouble in Paradise: How the ERCOT grid has changed over time, and the obstacles ahead, takes a holistic look at the complex challenges that face ERCOT in the coming years. To download your free extract from this report and explore these challenges in greater detail, simply fill out the form at the top of the page.
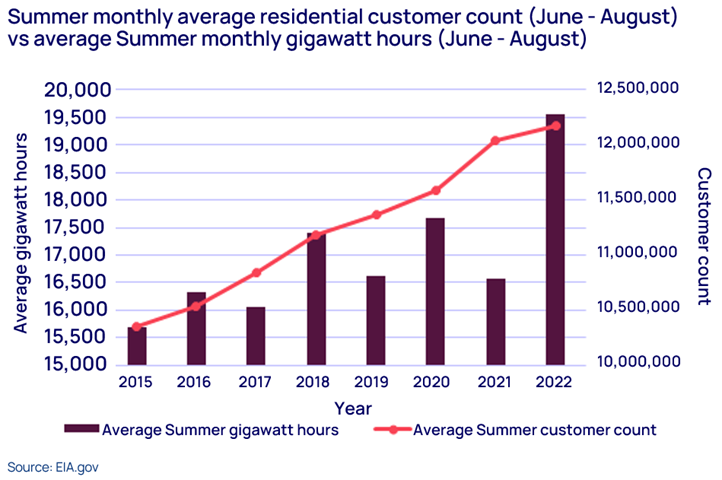
The report reveals that energy demand growth in recent years has been dramatic, with the average gigawatt-hours used each summer month, increasing by 3,856 GWH from 2015 to 2022, compared to the average monthly summer customers, which climbed by 1.8 million customers during the same period.
The NERC (North American Energy Reliability Corporation) is also forecasting growth in the ERCOT market including peak demand forecast rising 6%, nearly 4GW of new Solar PV capacity being added to the grid since 2022, and an 18% increase in the dispatchable demand response programs.
Even with this growth in resources, the NERC is calling for increases in dispatchable resources considering the load growth, potentially volatile and unpredictable weather conditions, and the decommissioning of 2.51 GW of coal units from since 2018 through 2023.
These challenges call out the need for increasing Peaker plants and renewable resources that contribute to a more sustainable and low-carbon power generation system. To this end:
- GT capacities across the grid have increased from 4.8 GW at the beginning of 2021 to around 7.5 GW by the end of 2022.
- Installed capacity of Solar PV has increased from 3 GW to 12GW since Spring 2020.
- Wind installations grew by 10.6 GW from Spring 2022 to Spring 2023, although the rate of growth is slowing.
- Energy storage capacity has increased from 163.2 MW to 2,981 MW from Spring 2020 to Spring 2023.
In the wake of the widespread power outages and market volatility caused by winter storm Uri in February 2021, ERCOT has implemented many actions to increase grid reliability. These include lowering the RT price cap from US$9,000/MWh to US$5,000/MWh, installing 10,000 new weatherization devices on critical equipment, upgrading 500 substations to withstand extreme weather conditions, installing 1,000 miles of new transmission lines and 500 new transformers.
The impact of these efforts includes improved stability with the hourly RT price peak going down from Spring 2022’s record of US$4,563 to US$768. Over US$1 billion in incentives to power generators from House Bill 1500 are also a vital part of ERCOT’s efforts to improve the reliability of the Texas power grid.
The problem of transmission congestion
In addition to the high growth in the ERCOT market, transmission congestion is also a challenge. Influenced by wind patterns, line outages, and the addition of new energy sources, congestion is most pronounced in the West region due to its high capacity of wind farms compared to other state regions.
The intermittency of renewable power sources
Congestion challenges are compounded by the unpredictability of wind generation in the ERCOT market. Based on the real-time West wind patterns, the West region could see completely different pricing risk and outcomes. Other regional congestion drivers include strong coastal wind periods in the South region that are often coupled with weak thermal generation response near the region, and congestion near the Houston region driven by line outages coupled with seasonal thermal outages.
The addition of new energy sources, such as solar nodes, can also lead to changes in transmission constraints. Large solar installations around the Houston and Dallas metro areas are redefining congestion in these regions and adding a solar or renewable component to typically thermal-driven congestion.
Energy storage is also bringing new constraints and considerations for managing congestion of the grid in the ERCOT territory. Batteries can quickly dispatch in seconds or minutes depending on the size, distance from the load, and state of charge, requiring a great deal of monitoring and optimization.
Wood Mackenzie’s PowerRT platform
In the face of the challenging ERCOT market, we are enhancing our PowerRT platform and North America Power Solutions tool to provide ERCOT market participants with growing analytical tools that bring additional transparency to RT generation across the grid. This includes market models’ sensitivities with access to a more significant number of renewable and thermal units that will increase the accuracy of market predictions and enable more effective decision-making for clients.
Our ERCOT desk monitors the daily ERCOT grid conditions to forecast energy prices, congestion, and weather risks. Much of this is enabled via access to our proprietary sensor network that monitors RT generation and transmission across Texas. The latest improvement to this tool, Modeled Unit Output (MUO), will increase visibility of newer renewable and thermal resources coming online, enabling faster and more accurate forecasts to support client’s daily trading decisions.
For more information on how we can help you, visit our North America Power Solutions page, and fill out the form at the top of the page to download a full extract from our recent report, Trouble in Paradise: How the ERCOT grid has changed over time, and the obstacles ahead.