Get in touch
-
Mark Thomtonmark.thomton@woodmac.com
+1 630 881 6885 -
Hla Myat Monhla.myatmon@woodmac.com
+65 8533 8860 -
Chris Bobachris.boba@woodmac.com
+44 7408 841129 -
Angélica Juárezangelica.juarez@woodmac.com
+5256 4171 1980 -
BIG PartnershipWoodMac@BigPartnership.co.uk
UK-based PR agency
ConocoPhillips acquisition of Marathon Oil creates third largest producer in the US Lower 48, says Wood Mackenzie
ConocoPhillips will produce 1.5M boe/d in the US Lower 48, renew commitment to Bakken and Eagle Ford
3 minute read
Addressing ConocoPhillips (COP) acquisition of Marathon Oil (MRO) in an all-stock transaction valued at US$22.5B, Alex Beeker, research director, corporate research for Wood Mackenzie said, “The addition of Marathon further solidifies ConocoPhillips in a league of its own, with few true peers. For ConocoPhillips, this is a diversified and balanced move across multiple geographies.”
According to Wood Mackenzie analysis, upon the addition of MRO's 390 kboe/d, COP will produce 2.3 million boe/d. This is more than TotalEnergies and nearly the same output as BP. Approximately 1.5 million boe/d will come from the US Lower 48, making it the third largest producer behind ExxonMobil and Chevron/Hess.
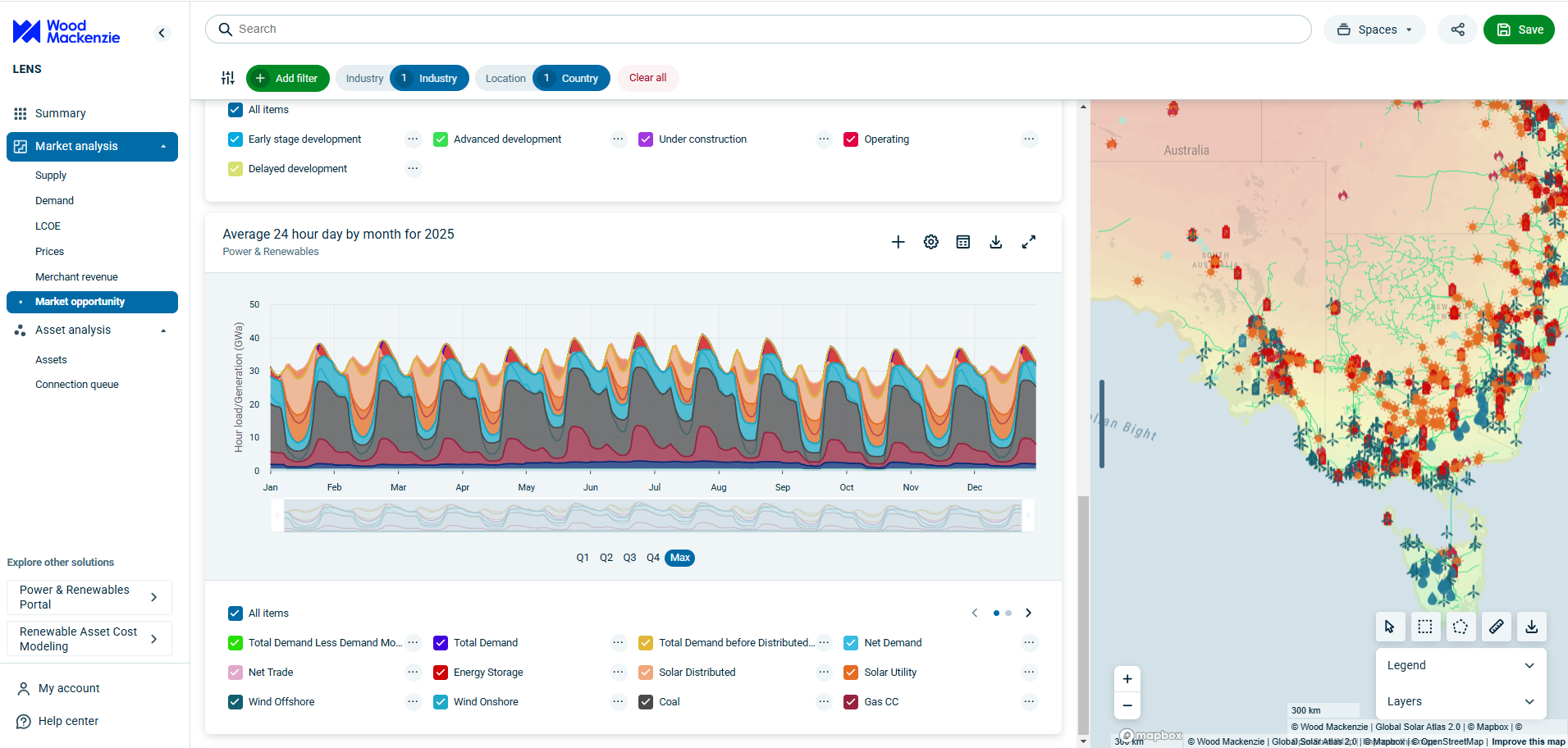
Continued Beeker, “Marathon provides ConocoPhillips with optionality and assets that immediately compete for capital. Marathon’s average well performance in the Bakken and Delaware over the past two years has exceeded ConocoPhillips. Upon closing, ConocoPhillips will become the largest Eagle Ford producer, a top three Bakken operator and remain a top five Delaware Basin player based on gross operated production.”
Wood Mackenzie estimates that the company expects to achieve US$500 million in annual synergies, with approximately half of the synergies coming through G&A savings, another US$150 million from operating costs and commercial optimization, and US$100 million from capital optimization through reducing activity in plays like the Bakken and shifting capital to the most productive areas.
Beeker noted that shareholder payouts will change as a result of the deal and may encourage other E&Ps to follow a similar path.
“The company is giving a vote of confidence to the deal by raising its base dividend by US$0.20/share or 34% following the deal’s closing,” said Beeker. “It is effectively rolling the variable dividend component of its VROC payout strategy into the base. Its base dividend payout ratio will rise from 16% to 21%, putting it ahead of EOG in terms of the most aggressive base dividend payout among the US Independents. For context, the US Majors pay out 25-30% of operating cash flow via base dividend.
Continued Beeker, “ConocoPhillips is always viewed as a leader in shareholder payouts. Do more US E&Ps now try to follow suit with leaning into buybacks and the base dividend while leaning away from special/variable dividends? The market is likely to reward companies with a higher base dividend as it gives confidence to investors in the longevity and stability of cash flows.”
Ryan Duman, director, Americas upstream for Wood Mackenzie, notes that the deal signifies a renewed commitment to the Bakken and Eagle Ford, contrasting with recent industry deals that focused solely on the Permian.
“Even though the deal increases ConocoPhillips’ Lower 48 concentration, the addition of Marathon’s non-Permian Lower 48 assets offers valuable diversification for the pro-forma entity,” said Duman. “Given ConocoPhillips’ impressive efficiency gains from activities like remote fracs and extensive use of simulfracs, we see significant potential for improvement on the Marathon assets. In the Eagle Ford, in particular, ConocoPhillips has been drilling roughly 50% faster than Marathon over the past year. And on top of that, its Eagle Ford wells have been over 10% more productive. In the Bakken, the story is slightly different but still encouraging. Marathon’s wells over the past two years have been about twice as productive as ConocoPhillips. So, the ability to transfer learning and improvements from both sides is significant and will likely materially improve non-Permian capital efficiency. While neither play will likely become a growth asset for ConocoPhillips, they will be able to provide good cash flow generation.”
Beeker added that benchmarking the new combined company comes with challenges.
“It’s significantly larger than other US E&Ps, but the lack of downstream and new energies businesses makes comparisons with the Majors difficult, too,” said Beeker. “Any mention of emissions reduction or low carbon investments as part of this deal was noticeably absent. With Major-like scale, will the company come under greater scrutiny to address energy transition risks? Chevron and ExxonMobil are pushing into CCUS, hydrogen and renewable fuels. But ConocoPhillips has devoted relatively minimal capital outside its legacy oil and gas business.
“We know ConocoPhillips is taking Scope 1 & 2 emissions reductions seriously, but the lack of a more robust energy transition strategy causes it to slip to the middle of the pack on our Corporate Resilience and Sustainability Index (CoRSI). The company ranks highly on cash flow longevity, margins and scale. But it lags its US Major counterparts on progress in low carbon energy.”