Get in touch
-
Mark Thomtonmark.thomton@woodmac.com
+1 630 881 6885 -
Hla Myat Monhla.myatmon@woodmac.com
+65 8533 8860 -
Chris Bobachris.boba@woodmac.com
+44 7408 841129 -
Angélica Juárezangelica.juarez@woodmac.com
+5256 4171 1980 -
BIG PartnershipWoodMac@BigPartnership.co.uk
UK-based PR agency
Renewables and nascent low-carbon technologies most exposed to high interest rates
Policymakers should focus on bolstering carbon markets, maximising subsidy efficiency and mobilising green finance
3 minute read
If high interest rates persist, transitioning to a net zero global economy will be even harder and more costly. The higher cost of borrowing negatively affects renewables and nascent technologies, compared to more established oil and gas, and metals and mining sectors, which remain somewhat insulated, according to latest report: ‘Conflicts of interest: the cost of investing in the energy transition in a high interest-rate era’ by Wood Mackenzie.
“Interest rates, which have risen sharply in the past two years, may not come down as far or as quickly as markets anticipate. This increased cost of capital has profound implications for the energy and natural resource industries, particularly the cost and pace of the transition to low-carbon technologies,” said Peter Martin, Wood Mackenzie’s Head of Economics and lead author of the report.
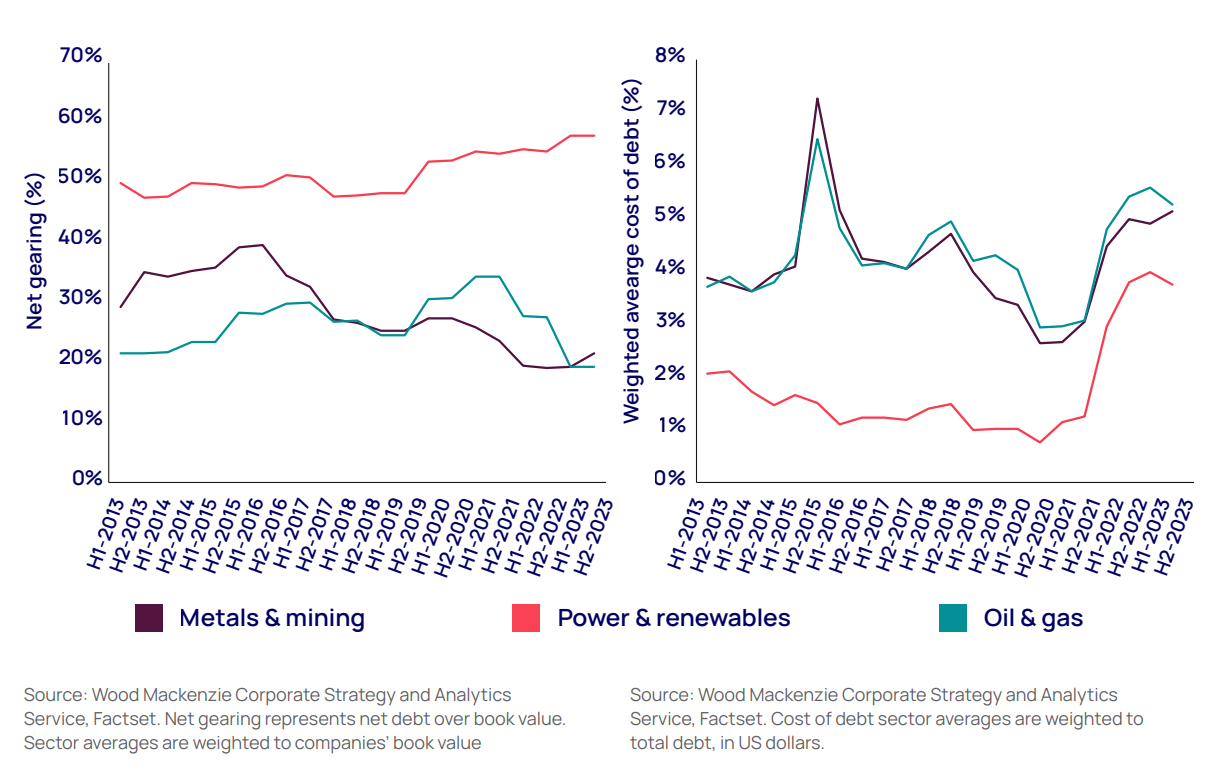
Higher interest rates disproportionately affect renewables and nuclear power. Their high capital intensity and low returns mean future projects will be at risk. In comparison, due to low gearing, many companies in the metals and mining and oil and gas sectors will be relatively unaffected by higher interest rates, stated the report.
In the US, Wood Mackenzie analysis shows that a 2-percentage point increase in the risk-free interest rate pushes up the levelised cost of electricity (LCOE) by as much as 20% for renewables. The comparative increase in LCOE for a combined-cycle gas turbine plant is only 11%.
Renewables have highest capital intensity of US generation (New York, 2024)
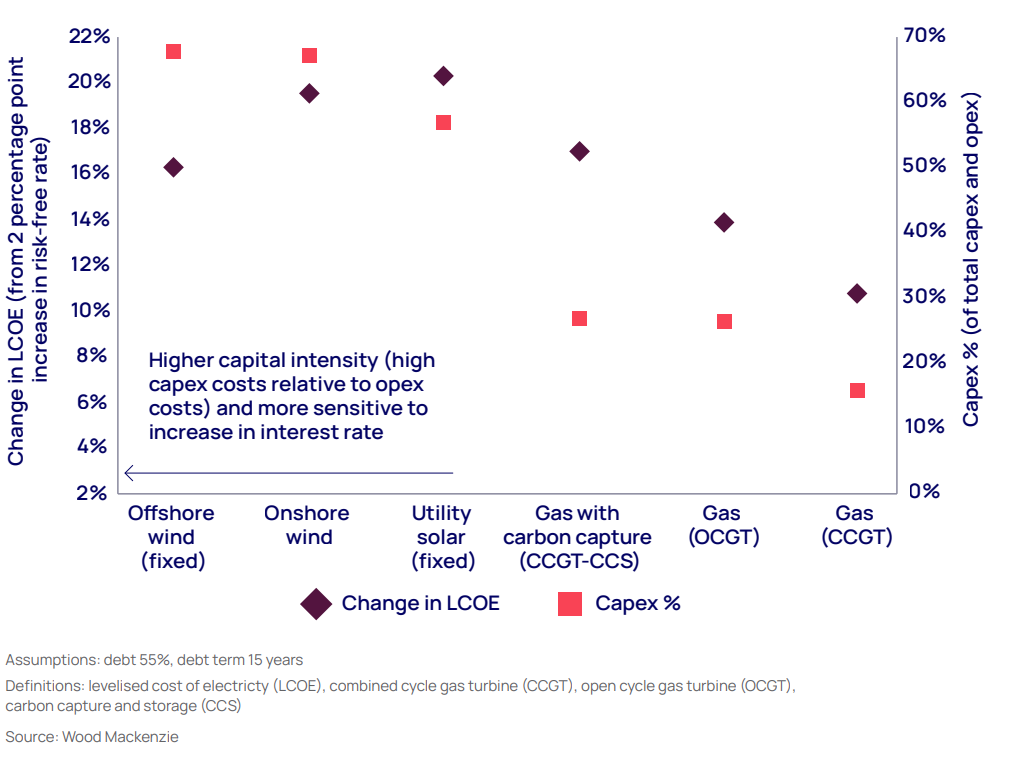
Higher interest rates also affect the competitiveness of renewables, stated the report. In many markets, onshore wind and solar have an economic advantage over hydrocarbon generation sources, even without subsidies in some cases. In the US, onshore wind can generate electricity at an LCOE of US$40/MWh, 50% of the cost of gas-fired generation. However, higher interest rates are eroding that advantage.
“While power and renewables companies have higher gearing, they do compare favourably with other peer groups on a cost-of-debt basis. But this is precisely what makes them more sensitive to interest rates. Mechanisms to reduce price and offtake risk enable power and renewables companies to obtain debt more cheaply than the relatively risky oil and gas and metals and mining sectors. The recent rise in interest rates, therefore, has a larger proportional impact on their cost of debt,” Martin said.
Cost of debt rising fastest for the highly geared power and renewables sector
Green tech under pressure
Nascent technologies, such as low-carbon hydrogen, carbon capture, utilisation, and storage (CCUS) and direct air capture (DAC), will play an important role in the energy transition. However, remarkable levels of capital investment and high capital intensity put these projects under threat amid higher interest rates, stated the report.
“The lack of economic incentives to capture carbon and the lack of a market for hydrogen are the most significant obstacles to investment in these sectors, but for projects that do progress, higher interest rates hurt the economics. This affects both smaller development companies that struggle to access debt and larger, credit-worthy emitters that rely on low-interest leverage to render projects attractive for shareholders,” Martin stated.
How can policymakers offset interest-rate headwinds?
The higher interest rate environment is a headwind to the energy transition globally, which is currently estimated to require US$75 trillion in investment if the world is to reach net zero by 2050.
“The good news is that there are actions policymakers can take now to help offset or at least mitigate the burden of higher interest rates. Policymakers need to remove obstacles such as slow permitting and project approval as well as offering clear, consistent, and sustained incentives, to support the uptake of low-carbon energy and nascent green technologies.”
In the report, Wood Mackenzie identified three policy priorities for policymakers:
- Focus on subsidy efficiency. With government finances under pressure, subsidies need to have the maximum impact on decarbonising the global economy. Targeted and non-discriminatory subsidies are most efficient, minimising nationalistic subsidy battles that are counterproductive to global emissions targets.
- Bolster carbon markets. First and foremost, conclude outstanding sections of Article 6 of the Paris Agreement, the original ‘rulebook’ on carbon markets and non-market approaches to mitigating global emissions.
- Mobilise climate finance. Greater use of financial mechanisms and instruments to maximise private-sector investment is needed. Central banks could offer loans to commercial banks at preferential rates, specifically to be used to finance low-carbon investments.