Get in touch
-
Mark Thomtonmark.thomton@woodmac.com
+1 630 881 6885 -
Hla Myat Monhla.myatmon@woodmac.com
+65 8533 8860 -
Chris Bobachris.boba@woodmac.com
+44 7408 841129 -
Angélica Juárezangelica.juarez@woodmac.com
+5256 4171 1980 -
BIG PartnershipWoodMac@BigPartnership.co.uk
UK-based PR agency
EV charger installations in the US are poised to grow fourfold by 2027
Tesla and ChargePoint continue to dominate the market, and brick-and-mortar stores are poised for growth
2 minute read
Wood Mackenzie estimates the number of charging ports in the US to reach close to 18 million by 2027, with most chargers in the residential category. However, the residential market share will slightly decline in that period as the public and commercial EV charging segments grow.
According to the inaugural North American EV charging infrastructure monitor, Tesla and ChargePoint dominate the market, with Tesla boasting a 61% market share of DCFC ports in the US, while ChargePoint leads with a 46% market share of level 2 ports in the US.
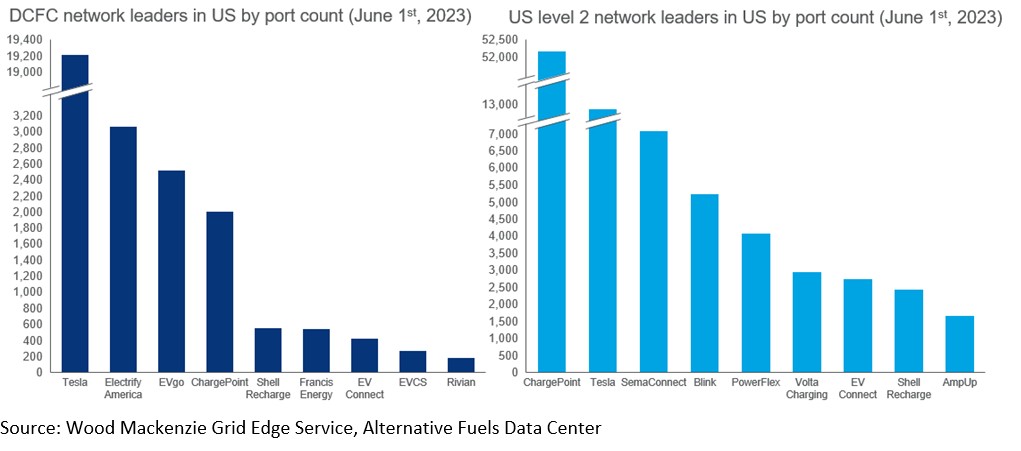
“Public EV charging networks are looking to establish and secure their footholds through aggressive expansion plans, innovative financing structures, and partnerships with automakers and other brick-and-mortar businesses,” said Nick Esch, Research Analyst, Wood Mackenzie.
Automakers continue to curate charging experiences
Recent announcements by automakers such as Ford, General Motors, and Rivian to adopt the North American Charging Standard (NACS) connector will give their drivers access to the Tesla Supercharger network. This signals the industry’s move toward Tesla’s formerly proprietary NACS, which has offered drivers a seamless and reliable charging experience. Charging equipment manufacturers such as ABB, ChargePoint, and Tritium have also announced that site hosts will have the option to add NACS ports on their hardware.
Growth opportunities for retail stores
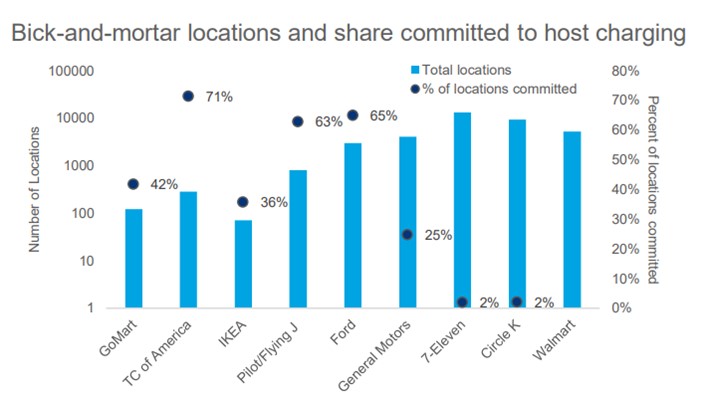
Deployment of EV charging infrastructure at brick-and-mortar locations offers major growth potential and remains an untapped market. Eligibility for the National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure grant program and proximity to population centers is driving retail store chains to deploy EV charging networks. Walmart intends to build its fast-charging network, potentially becoming the fifth-largest DCFC network in the US (based on current deployments).
“There is so much opportunity in the brick-and-mortar segment as it has synergies with EV charging,” said Amaiya Khardenavis, Analyst, EV Charging Infrastructure, Wood Mackenzie. “It is estimated that 85-90% of the US population lives within 10 miles of major retailers, making them very convenient charging locations for EV drivers. The stores seeking to increase customer dwell time will benefit from offering onsite EV charging, while stores that already enjoy high dwell time seek to earn additional revenue from charging.”
Electric school buses are the first movers in fleet electrification
Optimal duty cycles and substantial government funding are driving school bus electrification. Even though capacity upgrades needed to host charging infrastructure at depots can take months, the report notes that the growth of electrified school buses (ESBs) will drive more demand for charging infrastructure as well, with more than 4,000 ESBs receiving funding in Q4 of 2022, more than three times Q1 2022 totals.
Definitions
Level 2 ports – EV chargers with a charge rate between 3 kW and 19 kW of AC power.
DC fast-chargers (DCFC) – EV chargers that can achieve a charge rate between 50 kW and 350 kW.