Future energy – zero-carbon heating
Could heat pumps displace gas in our homes?
1 minute read
Simon Flowers
Chairman, Chief Analyst and author of The Edge

Simon Flowers
Chairman, Chief Analyst and author of The Edge
Simon is our Chief Analyst; he provides thought leadership on the trends and innovations shaping the energy industry.
View Simon Flowers's full profileFifty years ago, natural gas transformed homes with instant heat and hot water. But the days of gas and other fossil fuels dominating domestic fuels may be numbered. Rapidly evolving policy in the EU is searching for technologies to speed up electrification and decarbonisation.
Heat pumps could be part of the answer, binding households once and for all into reducing carbon emissions. Our experts in new energy technologies, Fei Wang and Ben Gallagher, and Murray Douglas, European gas, explained the options.
What is the technology?
Heat pumps are a proven technology, a heating and cooling system that’s ready for mass deployment. Two types are suitable for residential or commercial use – air source and ground source. Unlike a combustion boiler, they don’t produce heat but work like a fridge, transferring heat from a coil outside the building to a second coil inside using a refrigerant. The process can be reversed for air-conditioning in summer. They run on electricity, ideally zero-carbon renewables.
The big advantage is the heat pump’s exceptional energy conversion rate. A modern gas boiler has an efficiency rate of around 80%, with 20% lost in the process. Heat pumps can have 300% efficiency, generating 3kw of thermal energy for every 1 kilowatt consumed.
How big is the opportunity?
Huge. Over one-third of global energy demand is space heating in the residential and commercial sectors, served by a mix of fuels. Gas is the incumbent fuel in Europe (43%) and an important part of the mix in the US (40%), where electricity already has the biggest share (44%); while coal dominates in Poland and China. Oil and LPG are still widely used globally where communities are remote from gas infrastructure.
The penetration of heat pumps into the market today is minuscule. But the opportunity is massive – many multiples of the 20 million systems installed world-wide.
What’s holding heat pumps back?
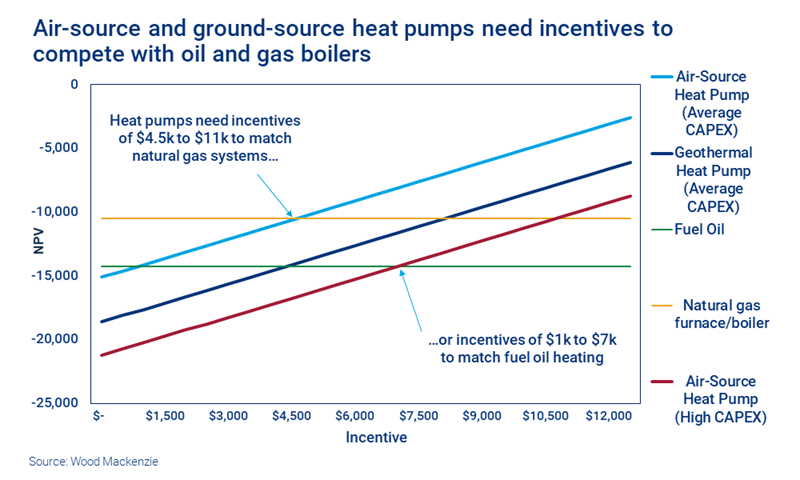
First, the upfront costs of installation. These can be up to US$15,000, about five times the cost of an average gas boiler. Yet the heat pump’s higher efficiency doesn’t fully compensate over the life of asset. New York state, for instance, has a cash incentive that makes it economical to switch from fuel oil, but it’s still not enough to beat gas.
Second, air source pumps, the cheaper of the two, see a decrease in energy efficiency as temperatures drop to sub-zero, though their performance in colder climates is improving. Ground source does work at low temperatures but is more expensive and needs outdoor space to lay the pipe system.
What’s the game changer for heat pumps?
All eyes are on European policymakers. The EU’s ‘Green Deal’ aims to accelerate the reduction in carbon emissions from 40% by 2030 to 50% to 55%. That won’t be achieved just by pushing coal out of the power mix – it needs to expand into non-power sectors. Some high energy-intensive industries like steel will take longer, so the focus has to be on transportation – and heating.
Residential and commercial space heating accounts for 11% of global emissions and is going to be in the crosshairs. Some European markets have already legislated against gas connections to new homes and commercial premises. The key question is whether heat pumps can make the big breakthrough to displace incumbent fossil fuel-based heating in existing homes. States in the US, including New York and California, are leading policy advocates of heat pumps.
The ability to reverse heat pumps is a real bonus. They can be a one-stop shop to decarbonise both heating and air-conditioning.
What are the implications for future gas and electricity consumption?
The EU’s 2030 targets are ambitious and may rely mostly on squeezing coal out of the power market. Heat pumps’ economics are just one barrier – the skilled workforce to roll out the systems at scale isn’t there yet. It could be that, like electric vehicles, heat pumps go mass market in the 2030s rather than this decade.
The potential loss of gas demand by 2040 could be substantial – we reckon as much as 25% lower in the residential sector to get on the pathway to reach the Green Deal’s ultimate goal of net-zero emissions by 2050. That’s around 50 bcm, or 10% of total demand, in the EU27 plus UK today. Meanwhile, switching from fossil fuels to heat pumps will drive up electricity demand, adding to pressure on power infrastructure.
Find out more about the electrification of heating
Our report The electrification of residential and commercial heating examines policies, technologies and costs to decarbonise the heating sector. Fill in the form at the top of this page for a complimentary copy of the executive summary.